5G smartphones are already on the market. The main advantages are extremely short signal propagation times (latency) and high download rates. The market study 'Thermal Management for 5G' published by IDTechEx in July 2020 highlights the challenges of 5G infrastructure systems and end devices with regard to thermal management.
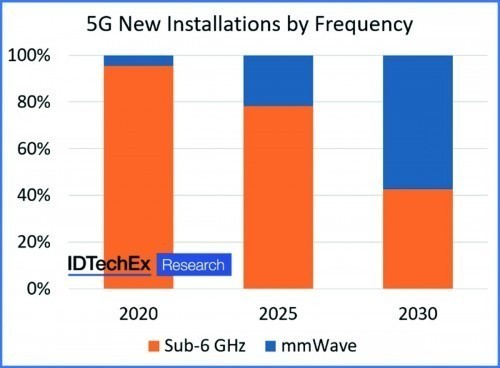
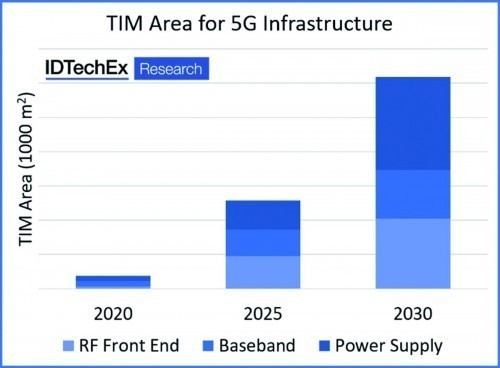
The extremely short signal propagation times (latency) and high download rates made possible by 5G are essential for time-critical and ultra-reliable data connections, for example in automated driving systems. Technology analyst Dr. James Edmondson, author of the study, refers to a report in the US publication 'PC Magazine' as background to his study, which deals with the availability of 4G (LTE) and 5G and their current download rates in various regions of the USA. No special insight: At the moment, 5G can only deliver on the promise of ultra-fast downloads at 2 Gbit/s in less than 5% of coverage areas. Either the millimeter wave spectrum or the sub-6 GHz range is used. According to the report, millimeter wave transmission enables faster downloads, but with shorter ranges. Sub-6 GHz transmission, on the other hand, is often even slower than the existing 4G operation. This leaves room for improvement in terms of the desired goal. Figure 1 shows IDTechEx's assessment of the further spread of 5G installations over the next ten years in terms of transmission frequency. At the heart of the study is the thermal management of 5G infrastructures and end devices. The reason: the higher frequency range requires a higher antenna gain in order to achieve the required ranges. The use of the millimeter wave spectrum reaches its limits when it comes to penetrating house walls or windows. This requires the use of antenna arrays in a compact design with densely packed components and a large number of transmit/receive stations in pico or femto format. Heat dissipation can take on critical proportions here, which requires the use of sophisticated cooling devices or cooling liquids. IDTechEx is developing an interesting market estimate for the development of the demand for thermal interface materials for the construction of future infrastructure systems in the 5G area. Figure 2 shows this estimated demand broken down by their use in RF front-ends, baseband processing and power supplies by 2030.
A decisive factor in the heat dissipation of components is the use of suitable materials as an intermediate layer between the component and the heat sink. This applies in particular to the HF front end. The growing use of 5G systems with their beamforming antennas based on the massive MIMO (multiple-input and multiple-output) principle and baseband processing with corresponding power supplies are likely to trigger the rapid further development of thermal management. The author notes that some of the first available 5G cell phones, especially the models operating in the millimeter wave range, tended to overheat at high download speeds and reverted to 4G mode to cool down. The manufacturers countered this effect with new thermal management solutions such as heat spreaders made of graphene.
The high signal amplification required by 5G systems therefore brings its own challenges in terms of thermal management. This also applies to power amplifiers with GaN components. It is true that their operating temperatures are generally higher than those of silicon-based systems. However, the higher power levels require the semiconductor components to be built using die attach. According to the author of the IDTechEx study, the growing use of GaN components, especially in sub-6 GHz systems, is leading to a shift away from conventional die attach processes based on AuSn towards new alternatives such as silver or copper sintering.
The IDTechEx study 'Thermal Management for 5G' includes a detailed analysis of the emerging 5G infrastructure market and its technological trends. It covers the frequencies used, the size of the transmitting stations and the MIMO principles and beamforming components, the power amplifiers and the semiconductor technologies and thermal interface (heat conducting) materials used. The study also covers 5G smartphones, some of which are shown in the form of "teardowns" to demonstrate their design. This analysis is complemented by another IDTechEx report on the topic: "5G Technology, Market and Forecasts 2020-2030". It covers the technologies, materials and innovations as well as vertical applications and the NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things).