The photoinitiators type 907 and type 369, which are used worldwide in solder resists for the structuring of printed circuit boards, are on the SVHC list (Substances of Very High Concern) due to their sometimes worrying risks to human health and the environment. Peters has developed solder resists that are free of these photoinitiators and are also ideal for direct exposure with LED or laser light sources.
![2-Methyl-1-[(4-methylthio)phenyl]-2-morpholinopropan-1-on 2-Methyl-1-[(4-methylthio)phenyl]-2-morpholinopropan-1-on](/images/stories/Redaktion_GT/thumbnails/thumb_morpholinopropan.jpg) 2-Methyl-1-[(4-methylthio)phenyl]-2-morpholinopropan-1-oneBackin 2012, photoinitiator 907 was initially classified as a category 1B reprotoxic substance by the industry on a voluntary basis and later by the European Chemical Agency (ECHA) with the 10th adaptation to technical progress in 2017. As a result, solder resists were labeled with the skull and crossbones symbol depending on the concentration in accordance with the then applicable Dangerous Substances Directive 1999/45/EC. At that time, Peters was increasingly looking for alternatives in order to soon be able to present solder resists that do not require the photoinitiator 907.
2-Methyl-1-[(4-methylthio)phenyl]-2-morpholinopropan-1-oneBackin 2012, photoinitiator 907 was initially classified as a category 1B reprotoxic substance by the industry on a voluntary basis and later by the European Chemical Agency (ECHA) with the 10th adaptation to technical progress in 2017. As a result, solder resists were labeled with the skull and crossbones symbol depending on the concentration in accordance with the then applicable Dangerous Substances Directive 1999/45/EC. At that time, Peters was increasingly looking for alternatives in order to soon be able to present solder resists that do not require the photoinitiator 907.
Substances on the SVHC candidate list are considered to be of concern because they are
- carcinogenic, mutagenic or toxic to reproduction
- persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic or
- very persistent and very bioaccumulative or
- are likely to have serious effects on human health or the environment (as endocrine disruptors).
After their inclusion in Annex XIV, i.e. the list of substances subject to authorization, these substances are subject to authorization and are therefore only authorized for certain applications for a limited period of time; use is permitted until a sunset date. Applications for authorization must be submitted no later than 18 months before the end of the transitional period.
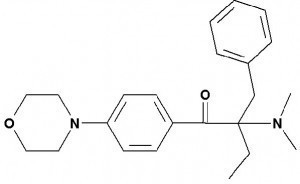 2-benzyl-2-dimethylamino-1-(4-morpholinophenyl)-butanone-1Thephotoinitiators 907 and also 369 were and still are the most commonly used photoinitiators in photo-structurable solder resists worldwide. Their classification as SVHC presents PCB manufacturers with the challenge of switching to photo-structurable solder resists with alternative photoinitiators.
2-benzyl-2-dimethylamino-1-(4-morpholinophenyl)-butanone-1Thephotoinitiators 907 and also 369 were and still are the most commonly used photoinitiators in photo-structurable solder resists worldwide. Their classification as SVHC presents PCB manufacturers with the challenge of switching to photo-structurable solder resists with alternative photoinitiators.
The polymerization initiated when the solder resist is exposed to light is not complete; even additional UV irradiation ('UV bumps') cannot have any effect here. As a result, condensate containing the photoinitiators, sometimes in the form of white powder or needles, can be found in the drying and curing ovens. In addition, photoinitiator 907 can be clearly identified in the AVT process in reflow soldering systems.
It is possible to completely dispense with these two photoinitiators mentioned above, and in particular with type 907, without any loss of performance. Shortly after the announcement of the new classification, Peters developed solder resists that are free of type 907 and type 369. For several years now, such Elpemer solder resists from Peters have been available, which are also ideally suited for direct exposure with LED or laser light sources. Many PCB manufacturers are now successfully using these products. As the ECHA has now included type 907 in the SVHC candidate list, the discussion about substitutes is picking up speed again. It therefore pays off that alternatives were developed at an early stage, for which there is already broad practical experience. Even with the new solder resists without photoinitiators, types 907 and 365, imaging accuracies of up to 50 µm can be achieved.
- high long-term temperature and thermal shock resistance up to 175 °C
- temperature-critical high-current applications
- excellent moisture insulation resistance (SIR) at 1000 V and
-
finest structures through direct exposure and contact exposure.
 Example of Elpemer Edition 766 dissolution capacity
Example of Elpemer Edition 766 dissolution capacity
The current discussion has sensitized electronics manufacturers and assemblers, and PCB manufacturers who switched to type 907-free solder resists at an early stage can now respond to the increasing number of inquiries from their customers in a relaxed manner.