As part of lecture strand 3, there were presentations on the topics of "Cost- and resource-efficient wastewater treatment" and, in a further lecture section, on "Complementary technologies".
Cost- and resource-efficient wastewater treatment
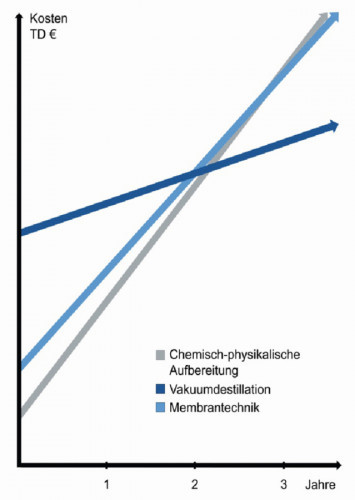 Cost comparison of various treatment methods (graphic for the presentation by Marius Straub, H2O)Dr. Elke Moosbach was scheduled to moderate this session, but was replaced by Dr. Martin Metzner. Laurens Wessels from MacDermid Envio Solutions opened the series of presentations with the topic "Advanced waste treatment for alkaline and acidic zinc-nickel waste". High-performance zinc-nickel coatings are becoming increasingly important as corrosion protection in many industries. After all, they extend the service life of many components made of steel. The disadvantage, however, is that the waste treatment of the process chemistry is more difficult than the usual alkaline or acidic zinc processes. The company has developed an innovative new approach that effectively treats both concentrated waste water and rinsing water.
Cost comparison of various treatment methods (graphic for the presentation by Marius Straub, H2O)Dr. Elke Moosbach was scheduled to moderate this session, but was replaced by Dr. Martin Metzner. Laurens Wessels from MacDermid Envio Solutions opened the series of presentations with the topic "Advanced waste treatment for alkaline and acidic zinc-nickel waste". High-performance zinc-nickel coatings are becoming increasingly important as corrosion protection in many industries. After all, they extend the service life of many components made of steel. The disadvantage, however, is that the waste treatment of the process chemistry is more difficult than the usual alkaline or acidic zinc processes. The company has developed an innovative new approach that effectively treats both concentrated waste water and rinsing water.
"Waste water treatment for zinc-nickel electrolytes"
The presentation by bi.bra Abwassertechnik GmbH focused on electroless nickel processes. Erik Bratfisch took to the stage on behalf of the company and introduced the audience to the treatment of waste using ion exchange technology - as an alternative to sulphide precipitation. Bratfisch explained that this would open up many opportunities for recovering valuable materials.
The Technical University of Ilmenau, together with Hillebrand Chemicals GmbH, reported on the advantages of inert anodes based on boron-doped diamond. The process has the advantage that the materials used form OH radicals due to the high oxygen overvoltage, which mineralize the complexing agents used in the wastewater. At the same time, metal ions are recovered from the wastewater stream on the cathode side. The background to this is the fact that the process solutions used in surface finishing are inevitably questionable and have to be treated later at great expense. Most of these purification processes are based on precipitation reactions, ion exchangers and vacuum evaporators. However, these processes do not deliver satisfactory results from a resource efficiency perspective. Greener solutions would be desirable. The speaker was Dr. Anna Endrikat.
"Focus on the recovery of recyclable materials"
The presentation "Process-integrated and additive environmental technology through diffusion analysis with spiral wound modules" (Rainer Klein, Spiraltec GmbH) gave a brief introduction to diffusion analysis for recycling process wastewater. Using a practical example, the speaker presented the process integration of the method and also focused on the recycling of valuable materials: both alkalis and acids can be recovered in this way.
"More ecological solutions for process water"
Sustainable wastewater treatment saves operating costs, a statement that no one can deny. One way to achieve this is vacuum distillation, said Marius Straub from H2O GmbH in Steinen, Baden. The process offers many advantages, including low operating costs, high quality and process reliability. In many cases, the recirculation of the water means that such a system would pay for itself in just two years.
"Vacuum distillation saves operating costs"
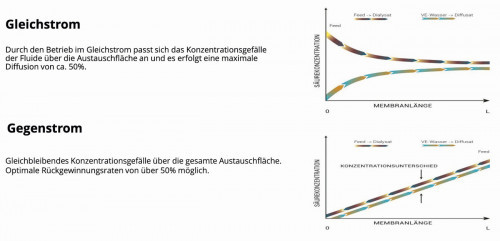 Diffusion analysis process (graphic from the presentation by Rainer Klein, Spiraltec)
Diffusion analysis process (graphic from the presentation by Rainer Klein, Spiraltec)
Erik Bratfisch (bi.bra Abwassertechnik GmbH) concluded the topic of "Cost- and resource-saving wastewater treatment" with a second presentation. It was about optimized sludge disposal in electroplating plants. Mixed sludge in particular is especially expensive to dispose of, he said, and exemplary cross-section scenarios show ways of optimization.
Complementary technologies
Monika Hofmann-Rinker (B+T K Alpha GmbH) gave a field report on the use of online analysis methods. She presented the advantages and disadvantages of the various analysis methods (online, atline, offline) and then critically evaluated the methods in terms of sustainability, quality assurance and the use of resources. The major advantage of online analysis compared to laboratory analysis is certainly the short time lag. This means that the chemical concentrations can be kept almost constant. This in turn keeps quality high and prevents financial losses due to rework.
 The topic area "Complementary technologies" was later moderated by Dr. Elke Moosbach; in this picture she can be seen together with Alireza Moazezi (contribution fem Edelmetalle undMetallchemie) (Photo. ZVO)
The topic area "Complementary technologies" was later moderated by Dr. Elke Moosbach; in this picture she can be seen together with Alireza Moazezi (contribution fem Edelmetalle undMetallchemie) (Photo. ZVO)
fem Edelmetalle und Metallchemie sent Alireza Moazezi into the race with the presentation "Innovation in zinc die casting - producing mirror-finish casting surfaces through release agent-free production". Mirror-polished cast surfaces play a role in many areas, including and above all in the automotive, furniture and electrical industries. The production of mirror-finish cast surfaces can be optimized. This is achieved by avoiding the use of release agents. The absence of release agents reduces the porosity of the cast parts and increases surface cleanliness. This enables thinner bright coatings, e.g. bright copper from cyanide copper, bright copper, nickel and chrome
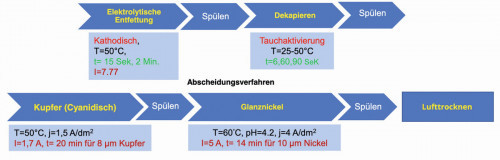 Further processing of release agent-free castings (lecture by Alireza Moazezi, fem)
Further processing of release agent-free castings (lecture by Alireza Moazezi, fem)
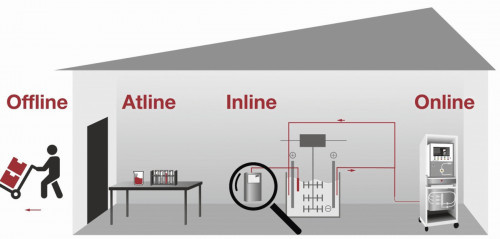 Analyses: The time factor is decisive (presentation by Monika Hofmann B+T K Alpha)
Analyses: The time factor is decisive (presentation by Monika Hofmann B+T K Alpha)
The presentation by Dr. Adolphe Foyet from DuPont focused on silver surfaces from acid electrolytes, before Mathias Fritz took over for the TU Ilmenau. His lecture dealt with light-induced platinum depositions for semiconductor components. Metal-semiconductor compounds play a major role in microelectronics. Silicon platinum semiconductor contacts are often used. These are applied using sputtering technology or by heat treatment of printing pastes. Fritz presented an electroplating approach, focusing on the pre-treatment of the silicon by illumination.
Frank Simchen from TU Leipzig then presented a way of identifying parasitic electrotechnical sub-processes - namely in the plasma-electrolytic oxidation of magnesium. This is an innovative, environmentally friendly method for surface refinement of light metals. Put simply, the component to be treated undergoes strong anodic polarization in a special electrolyte. This leads to spark discharges that strike the substrate from the electrolyte. This results in the formation of a protective oxide ceramic layer, the quality of which has been identified and described.
Finally, Lucia Nascimento from TU Ilmenau spoke once again. Her topic was the electropolishing of precious metal alloys in ionic liquids. The background to this is the fact that mechanical polishing processes reach their limits with components of complex geometry - especially with regard to the achievable surface quality (Ra in the range of 60 to 100 nm). Additively manufactured components also require polishing methods other than mechanical ones. Precious metals can be dissolved anodically in ionic liquids and recovered again cathodically. Studies at Ilmenau Technical University have shown that it is possible to electropolish precious metals in a mixture of choline chloride and ethylene glycol.


