In the coming years, a growing number of designers and circuit developers will increasingly have to deal with the fundamentals of wireless technology, many of them for the first time.
The reason for this is the advance of IoT, smart wearables and other miniaturized electronics with wireless information transmission. Antennas play an important role in this. To provide assistance, Antenova offers an ever-growing range of miniaturized antennas of all kinds as well as additional services and numerous information options. This article provides an overview.
The British company Antenova was founded in 1999 and offers hardware and services for wireless information transmission worldwide [1]. The focus is on miniaturized antennas for IT devices of all kinds. Antenova sees itself as the market leader in this product sector. The antenna range is constantly being expanded to provide high-performance solutions for the latest wireless connectivity requirements. One example of this is the ongoing triumph of wearables. Not only has it brought with it a new area of business, but it has also led to unprecedented new, higher demands on antenna solutions in terms of design, materials and reliability. Another example is the demands on wireless transmission technology resulting from the massive transition to M2M and IoT applications. Here, too, new, reliable and cost-effective antenna solutions are required. Figure 1 shows that antennas are the critical components of a transmitter (TX) and receiver (RX) wireless system [2].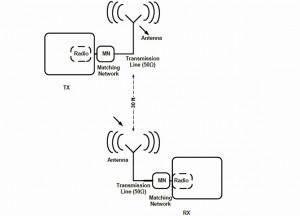 Fig. 1: Typical short-range wireless radio system
Fig. 1: Typical short-range wireless radio system
High product requirements, large product variety
Antenova supplies leading module suppliers and system integrators. Key considerations for the company's standard antenna solutions, which are required for wireless M2M, IoT and embedded electronics applications, are
- high efficiency
- low power consumption
- reliable performance
- Easy automated assembly
- Small customized designs
The Hatfield-based company covers a wide range of applications with its products: GSM, CDMA, 3G, 4G, 5G, LTE, GPS, GLONASS, Beidou, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, ISM and NB-IoT. Antenova won a hardware award at Embedded World 2018, for example, for its high antenna quality.
The range of applications mentioned already suggests that Antenova serves customers all over the world and therefore also has branches in Taiwan and China, for example. The standard antenna series for WLAN, Wi-Fi, GPS, ISM and telecommunications applications are considered leaders in their markets. New antennas for new M2M and IoT applications are constantly being added. The product range is divided into seven groups:
- gigaNOVA - original range of embedded miniature antennas
- lamiiANT - family of SMD antennas manufactured from FR4 materials
- flexiiANT - group of flexible FPC antennas with a cable and connector attached to the underside or housing of a product
- terminal antennas - slim ergonomic antennas of high performance in a stylish design
- RADIONOVA - high-performance antenna modules for wireless M2M and embedded applications
- ceriiANT - family of miniature ceramic antennas that are among the smallest antennas in the world
- REFLEKTOR - antennas for operation without detuning on metal surfaces or when the product housing is mainly made of metal.
Some types of antennas are briefly presented below.
 Fig. 2: GNSS M20047-1 active antenna for global navigation satellite systems
Fig. 2: GNSS M20047-1 active antenna for global navigation satellite systems
GNSS M20047-1
Receiver for global navigationsatellite systems (GNSS). The active antenna comprises the complete antenna and the front end(Fig. 2).
- Frequency range: 1559-1609 MHz
- Efficiency: 65 %
- Dimensions: 7.0 x 7.0 x 0.9 mm
 Fig. 3: Beltii antenna for global navigation satellite systems
Fig. 3: Beltii antenna for global navigation satellite systems
Belti i
Receiver for global navigation satellite systems (GNSS). A small antenna that is suitable for small designs and works with all GNSS satellite constellations. It can be integrated into the corner of a PCB without the need for GNS spacing. The high detuning resistance makes it the ideal choice for small handheld and even wearable devices(Fig. 3).
- Frequency range: 1559-1609 MHz
- Efficiency: 60 %
- Dimensions: 15.6 x 3.3 x 4.4 mm
Recent antenna developments
The range of antennas is constantly being adapted in line with advances in electronics. At the beginning of July this year, Antenova launched Lutosa, a compact high-performance antenna for the 5G bands that can be used worldwide, including band 74 (1420-1520 MHz) and band 71 (617-698 MHz)(Fig. 5). It is part of the flexiiANT family mentioned above. Fig. 5: Lutosa antenna for the 5G band and other ranges
Fig. 5: Lutosa antenna for the 5G band and other ranges
Lutosa is a flexible antenna measuring 95x15x0.15 mm and is ideal for smaller designs as it can be bent or folded and inserted into the device. The antenna is linearly polarized and has shown high efficiency in tests. Antenova has developed this solution for easy integration into a device. The antenna does not require grounding or a suitable network and is simply attached with its own self-adhesive strip. It is intended for the next generation of M2M and IoT applications that utilize video streaming and high data rates in the 5G networks. This antenna will be suitable for autonomous vehicles, cellular Wi-Fi hotspots, urban delivery drones and CCTV over 5G.
Lepida SR4L054, a high-performance 5G broadband antenna in SMD design, was added last fall and is designed for high efficiency and high performance across the entire spectrum from 600MHz to 3800MHz(Fig. 6). Fig. 6: High-performance 5G broadband antenna in SMD design Lepida SR4L054
Fig. 6: High-performance 5G broadband antenna in SMD design Lepida SR4L054
CEO Paul Hill commented: "Lepida targets the growing 5G market and marks the continuation of a successful period for Antenova. Sales have held up well for us despite Covid. Our company is in good shape to capitalize on the increasing opportunities of 5G."
Back in summer 2019, the company added Minuta, a new ultra-compact dual-band Wi-Fi antenna, to its range of tiny embedded antennas. Minuta is a ceramic antenna measuring 1.0 x 0.5 x 0.5 mm, making it one of the smallest embedded antennas available today. Antenova has developed this antenna for the newer 4.9-5.9GHz frequency band, which is less disturbed than the 2.4-2.5GHz range and offers better performance with less interference. However, it serves both ranges(Fig. 7). Minuta is part of the CeriiANT family. Fig. 7: Ultra-compact dual-band Wi-Fi antenna Minuta
Fig. 7: Ultra-compact dual-band Wi-Fi antenna Minuta
Minuta gives designers useful flexibility in the layout of a PCB as it does not have to be placed at a corner but can be placed along one of the long edges of a PCB. The antenna is ideal for access points and portable devices. The manufacturer recommends Minuta especially for wearable technology and body-worn devices, as it is less prone to detuning when used close to the human body.
Great knowledge required
Antennas are unlike any other type of integrated circuit. To achieve a high level of performance, they require an optimized operating environment. Here are some factors to consider when starting a PCB design:
- Miniaturization
- Component layout
- Antenna package spacing
- Ground plane positioning
- Housing material of the device
- Via design
To achieve the best results in a particular application, the designer of the assembly or final device must have some understanding of the possible effects of the antenna's configuration on RF performance(Fig. 8). Once he has decided on a particular configuration, the performance of the antenna can be optimized by measuring its input impedance in situ and designing an appropriate circuit match to operate the RF chip with a 50 ohm load impedance, for example. Fig. 8: The arrangement of an antenna in an assembly requires great care
Fig. 8: The arrangement of an antenna in an assembly requires great care
In an application note for antennas of the gigaNOVA series for the mobile radio sector, circuit board designers are given some tips on what they have to pay attention to when designing the circuit board or the module and also the final device [3]. The starting point for the instructions is that the mobile radio antennas in this series are usually very small: their longest dimension is much shorter than a quarter of the wavelength of the signal to be processed. The first task is to select the correct antenna for the application and to place the antenna on the corresponding module. In [3], for example, a note is given for the correct positioning of the antenna on the PCB according to Figure 9 so that the antenna function is not negatively affected.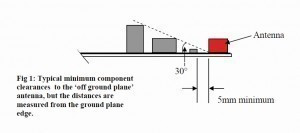 Fig. 9: Note for the correct placement of an antenna from Antenova's gigaNOVA series
Fig. 9: Note for the correct placement of an antenna from Antenova's gigaNOVA series
Violation of the suggested limit leads to a progressive reduction of the impedance bandwidth of the antenna and to an increased risk of loss of RF energy due to coupling into other circuit parts. Due to the interactions between the antenna, the PCB dimensions and the respective layout, component types and circuit functions of the relevant components, it is very difficult to give hard quantitative guidelines. Detailed electromagnetic modeling is possible, but it is very expensive to model a complex circuit in the required detail, especially if some of the interactions involve complex digital ICs.
The antennas are mounted in an area that is free of copper ground planes of the PCB. They generate electromagnetic fields of equal intensity on both sides of the PCB on which they are mounted. This results in some basic requirements for the designer, which at first glance seem quite trivial:
- Never place ground planes or conductor runs under the antenna
- Never place the antenna in the immediate vicinity of metallic objects
- In the final device, cables and components must not come too close to the antenna
- Monopole antennas such as Reflexus and Calvus require an adequate ground plane to be efficient
- Final tuning must always be carried out in the housing of the end product, i.e. not outdoors
- Never use an antenna with a completely different layout to the reference design and expect it to work without tuning
- Do not use metal housings or metallized plastic around the antenna
- Test the plastic housing for high RF losses, preferably before production
- Never use low Q loading components and do not change manufacturers without retesting
- Do not use very narrow traces. They should be relatively wide if space permits.
Services
As wireless transmission technology moves into more and more products as part of the transition to smart factories, IoT, wearabless, smart homes, etc., a growing number of designers and circuit developers are also having to deal with the fundamentals of wireless technology, many of them for the first time. To support them in their work, Antenova offers an ever-growing standard range of antennas as well as other services such as
- Antenna alignment and testing
- Support for the customer's product development cycle
- Customized antenna design in case of individual solutions.
Antenova's antennas are specifically designed for integration into a wireless communication device. The company refers to this design philosophy as Design for Integration (DFI). On request, the company provides CAD files for all its antennas free of charge to facilitate the integration of the antenna in the design phase. CAD files can be downloaded from the relevant product pages. Antenova also offers free architectural and Gerber reviews.
Further support
Printed circuit board designers and circuit developers can find additional help and information on Antenova's website in various forms such as
- Downloadable technical articles on the basics of board design for wireless products [4]
- Webinar videos, e.g. 'How to choose the right antenna: An Introduction' from July 19, 2021. in June/July 2021 there was a whole series of webinars on various topics, in May 2021 a webinar on designing medical devices with wireless communication [5]
- Antenna Quick Guides
- Case studies
- White papers for download, e.g. 'The Ultimate Guide to Impedance Matching'.
A transmission line calculator is also available for free download. This provides interested parties with help for quick, easy and flexible options when selecting the optimum transmission line dimensions. Antenova's blog also has an article on basic design considerations for wireless eHealth devices. It says: "Designing any new product has its challenges, but eHealth devices operate in a particularly challenging environment. Aside from the usual issues with RF legislation, the regulatory environment for healthcare technology is quite complex, and the users themselves often have specific requirements. Furthermore, these devices can be used in life and death situations, so their reliability must meet the highest standards. As a result, the development of eHealth devices requires more care and planning than many other systems.
New free tool for placing antennas on printed circuit boards
In May 2021, Antenova announced that it has developed a new software tool to help designers place antennas in a wireless design. The Antenna Selection & Placement Tool shows the optimal position for embedded antennas on the PCB, depending on the dimensions of the PCB and the specifications of the antennas [6](Fig. 10). It places each individual antenna on the PCB in the best position for signal strength. The company has developed this tool to support product designers who do not have access to in-house antenna knowledge. Fig. 10: Antenova's new tool helps with the placement of multiple antennas on a board
Fig. 10: Antenova's new tool helps with the placement of multiple antennas on a board
The tool is designed to help designers place the antenna in the best position early in the design process and more easily achieve a working wireless design. It can be used for a single antenna or for up to three antennas, as newer devices often require multiple antenna types to be installed. Antenna placement becomes more complex when there is more than one antenna in the design, as each antenna must be able to radiate correctly without causing interference with the others. For this reason, you can group up to three antennas from different categories or a pair of antennas in a diversity configuration.
Antenova's placement tool will be valuable for designers creating layouts for the small PCBs in some of the latest trackers and mobile devices. The tool not only shows the best position for the antenna, but also the 'keep-out' area next to the antenna that needs to be kept clear of other components. In this way, it helps designers to pack the components as tightly as possible and save space in the design.
"RF engineering skills are in short supply, and not all designers have access to antenna specialists. That's why we offer our Antenna Placement Tool to help designers get started with their wireless design and achieve a successful layout right away," explained Michael Castle from Antenova. The tool is available on the blog at [7]. There is also a short introductory article there.
References:
[1] www.antenova.com
[2] www.cypress.com
[3] www.glynstore.com/content/docs/antenova/Cellular_gigaNOVA-09MD-0024-2-AN.pdf
[4] https://blog.antenova.com/board-design-for-wireless-products
[5] https://blog.antenova.com/topic/webinars
[6] www.electronicsweekly.com/news/business/free-tool-placing- antenna-pcb-2021-05/
[7] blog.antenova.com/how-to-use-antenna-selection-placement-tool