It is not immediately visible, but creeps in and every production manager is happy if it does not appear: We are talking about unwanted oxidation, or rust. With a combination of the right plant technology and a passivation process developed by Borer Chemie AG in Zuchwil, Switzerland, products can be effectively protected during the manufacturing process.
Ensuring corrosion resistance on metallic materials is a prerequisite for preventing unwanted oxidation. This passivation process guarantees the permanent legibility of product markings for clear traceability and permanent corrosion resistance. In addition, complex shapes, demanding materials and new technologies such as additive manufacturing pose a particular challenge.
But what exactly is passivation? The process is often associated with surface protection such as coating (anodizing, anodizing, burnishing, etc.), an oil layer on the metal surface or similar applications. However, this application has nothing in common with actual passivation. Passivation is a conditioning process. In surface technology, this means that a protective layer forms spontaneously on a metallic material by using the right medium (e.g. deconex MT 41) or that this is created in a targeted manner. This protective layer prevents corrosion of the base material or slows it down considerably.
Successful passivation with the right preparation
Metallic products that need to guarantee long-lasting protection for their future use are chemically passivated. Before passivation, however, it is essential to create a clean and residue-free surface. High-quality pre-cleaning is so important because the passivation media can only force a reaction at the points where direct contact with the metallic surface is ensured. Even passivation cannot ensure lasting protection if the surface is not clean before passivation.
Borer Chemie AG has developed its own deconex cleaning concept, including passivation, to meet the high demands of the production process. This can be used on different system technologies such as immersion, spraying and vacuum processes. The cleaning concept is based on a structured 7-step procedure, with which the customer's requirements are recorded and on this basis a cleaning and passivation process optimized for the individual customer's needs is developed (Fig. 1). The material compatibility tests showed good compatibility with numerous types of stainless steel as well as copper, bronze, aluminum and titanium. Plastics, such as ABS, which is predominantly used in plastic electroplating, are also compatible with deconex MT 41.
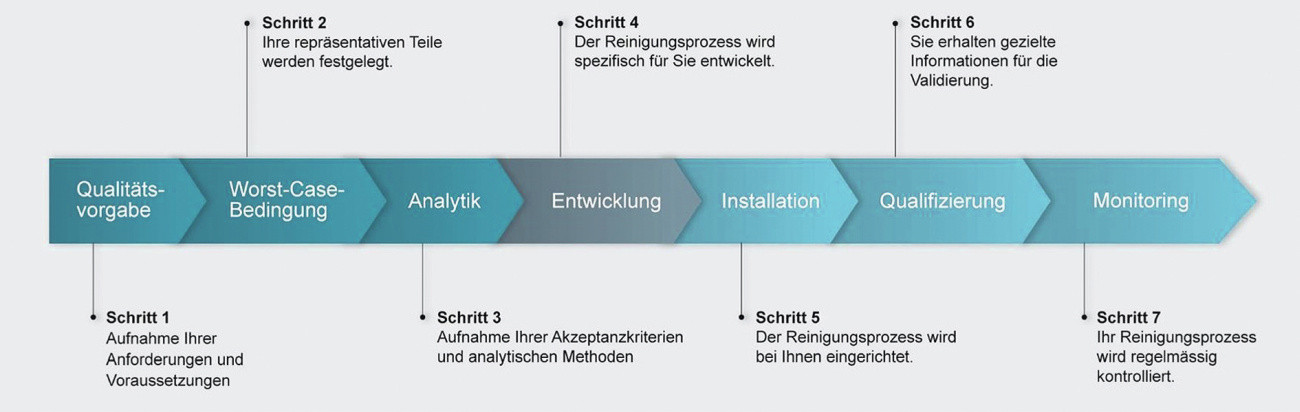 Fig. 1: 7-step procedure for structured process development
Fig. 1: 7-step procedure for structured process development
The deconex cleaning agents take into account the high requirement standards of the manufacturers and are developed on a customer-specific basis and implemented at the customer's site. Depending on the industry, these cleaning agents are completely free of difficult-to-rinse and undesirable ingredients. On the one hand, this greatly reduces the risk of contamination from the process media and, on the other, ensures process reliability as residues (process chemicals and production residues) are optimally removed. Finally, the process leads to reproducible results.
The passivation solution deconex MT 41
The innovative passivation process differs significantly from the conventional nitric (nitric acid) and citric (citric acid) processes known on the market. Deconex MT 41 is a strongly acidic passivating agent with a pH value of 2.2, which consists of a phosphoric and nitric acid component as well as non-ionic surfactants. The advantage of this passivation solution is that it can be used in much lower concentrations compared to nitric (HNO3) immersion passivation. Thanks to the lower concentration of 0.02 to 0.12% by volume, the passivation solution can be used both for conventional immersion passivation and for the new, more economical spray passivation and especially for passivation in a vacuum process. The temperature range extends from 20 to 85 °C. High temperatures are generally interesting for the efficiency of the passivation process, as the chemical effectiveness increases at higher temperatures. Conventional passivation processes based on nitric acid cannot be used in a vacuum or spray process due to the temperature variables, gas formation and foaming behavior - a safe application would be unlikely.
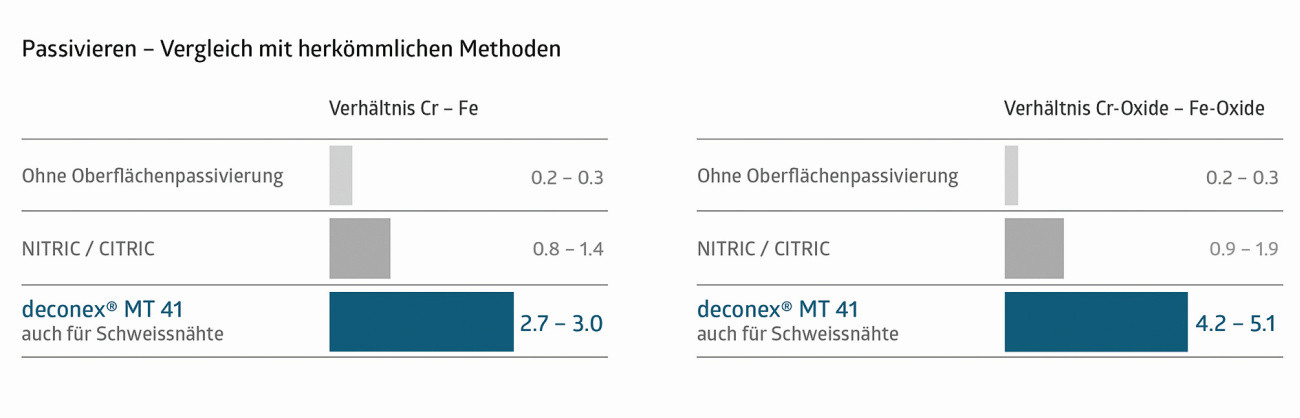 Fig. 2: Passivation - comparison with conventional methods
Fig. 2: Passivation - comparison with conventional methods
Compared to conventional immersion passivation with nitric acid, the new process is both more economical and more environmentally and user-friendly. The solution is easily biodegradable and thanks to its low concentration - depending on local wastewater regulations - can be neutralized and disposed of via the normal wastewater system.
Application examples
Table 1 shows the application parameters for the spraying process and Table 2 for the immersion process. The passivation process developed by Borer Chemie was compared with other passivation media from an economic and ecological point of view as well as in terms of material compatibility and shows a measurable added value. In addition, passivation with deconex MT 41 was compared with conventional passivation processes in terms of the formation and characteristics of the oxide layer. This resulted in the findings in Figure 2, which show that an excellent ratio of Cr - Fe and Cr oxide - Fe oxide was formed on the surface compared to the application with nitric/citric. The results achieved with deconex MT 41 can also be used as a reference for weld seams, which are comparable in principle to additive manufacturing.
|
Process example for the spray application |
Dosage |
Temperature |
Exposure time |
|
Primary passivation (long-term passivation) |
2 % |
RT - 85 °C |
30-60 min. |
|
Secondary passivation (short-term passivation). |
2 % |
RT - 85 °C |
5-30 min. |
|
Process example for immersion application |
Dosing |
Temperature |
Exposure time |
|
Primary passivation (long-term passivation) |
8-12 % |
RT - 85 °C |
30-60 min. |
|
Secondary passivation (short-term passivation). |
8-12 % |
RT - 85 °C |
1-30 min. |
Advantages compared to nitric acid
Nitric acid is a proven process medium for passivation, which ensures the passivation of the metal surface. Its advantages and disadvantages are well known: For example, it is recognized that if the oxide layer is well formed, the process is qualified in medical technology, for example, in accordance with the ASTM A967 standard. The known disadvantages of nitric acid include the loss of contrast in markings and, as a result, reduced legibility, the formation of nitrous gases, a high concentration of chemicals and complex waste water and exhaust air treatment. In all these cases, the use of deconex MT 41 brings added value to the passivation process.
|
Nitric acid (Nitric) |
deconex® MT 41 |
|
Chemicals |
|
|
Nitric acid |
Nitric acid, phosphoric acid, non-ionic surfactants |
|
Nitric acid Concentration in the process tank between 20 and 45 % |
Chemical concentration from 0.02 to 0.12 % concentration in the process tank |
|
- In principle, both processes fulfill the requirements of the ASTM A967 standard. However, deconex MT 41 puts less stress on the material and the labeling and legibility is guaranteed. |
|
|
System technology |
|
|
Process container made of PVDF |
Process tank made of PVDF or stainless steel |
|
Only applicable in immersion process |
Can be used in immersion, spray and vacuum processes |
|
Existing equipment can be used for the application of deconex MT 41. In addition, it is now possible to use the passivation process in a spraying or vacuum process. This offers new possibilities for process design, e.g. cleaning and passivation in a sluice function. |
|
|
Material compatibility |
|
|
Stainless steel, titanium and titanium alloys |
Stainless steel, titanium, titanium alloys, carbon, PEEK, silicone, Teflon, various plastics |
|
Material compatibility is another added value that can be used to optimize production processes. Products that are already fully assembled and have different materials can be passivated as a whole. Here we are talking about instruments that have a combination of stainless steel, titanium, titanium alloys, carbon, PEEK, silicone, Teflon, various plastics, etc. |
|
|
Rinsability (removal of chemicals) |
|
|
Poor rinsing behavior due to high concentration, risk of acid residues/stains, oxidation |
Excellent rinsing behavior due to low concentration, low risk of acid residues |
|
Everything that is applied to the surface must also be able to be removed again, including the chemicals. Due to its composition and low concentration, the product is easy to rinse off and therefore ensures residue-free cleaning/passivation. In addition, no neutralization (decapitation) is required when using deconex MT 41. |
|
|
Waste water treatment |
|
|
Neutralization and precipitation of heavy metals required |
deconex MT 41 can be neutralized and disposed of in accordance with the law |
|
Depending on the process application and the service life of the process tanks, the precipitation of heavy metals can be dispensed with in the wastewater treatment of deconex MT 41. |
|
The comparison of the passivation media nitric acid and deconex MT 41 in Table 3 shows the advantages of using deconex MT 41. This brings new application possibilities and advantages in the passivation process which are not fulfilled by passivation with nitric acid:
- deconex MT 41 is the only passivation medium that allows application in a vacuum process.
- Application by spraying
- High/wide material compatibility
- Application at low concentration
- Very low nitrous gas formation
- Cleaning and passivation possible in the same working chamber (spray application)
- Can be used in a sluice function.


