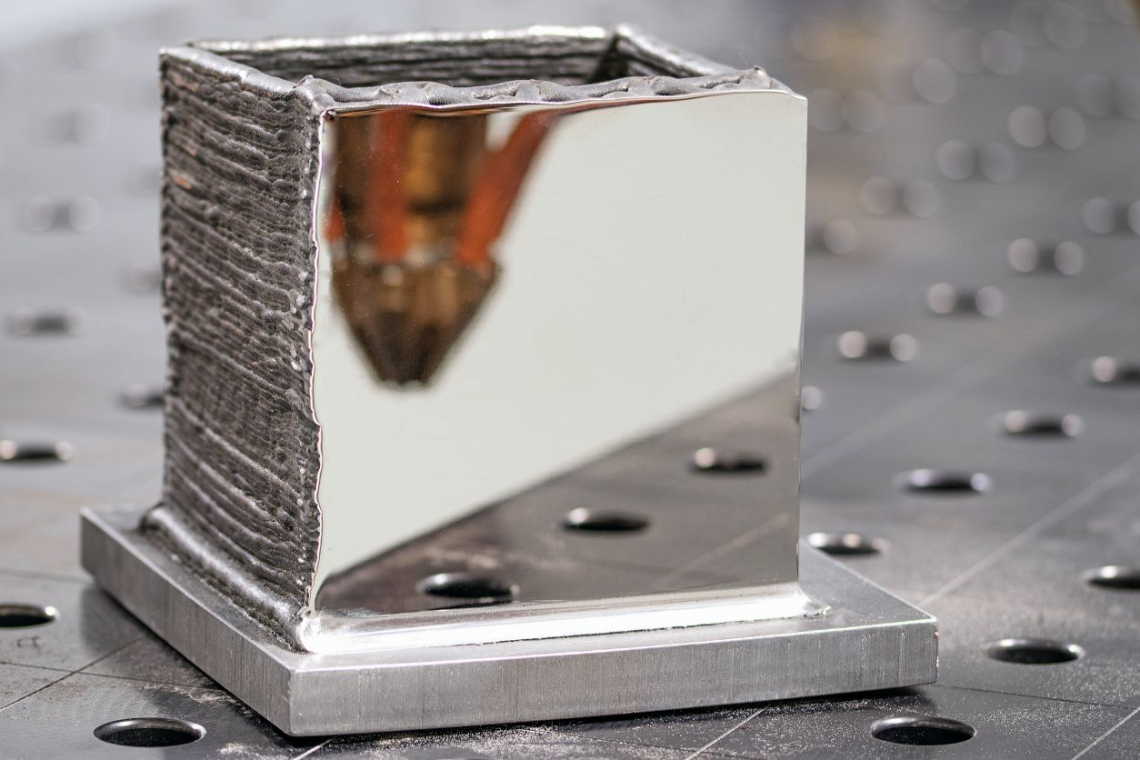
Coating cast iron with stainless steel is a key issue in industries that place high demands on corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. Cast iron is frequently used due to its excellent damping properties and cost efficiency, but shows weaknesses in corrosive environments. Tool and plant manufacturer Meissner AG has developed a special laser metal deposition (LMD) technology to meet these challenges.
Initial situation: cast iron in industrial applications
Due to its microstructural properties, cast iron is able to dampen vibrations and is therefore the preferred material for machine stands or base frames in sectors such as the food industry, mechanical engineering and the automotive industry. However, cast iron is susceptible to corrosion in damp and chemically contaminated environments, which is a serious problem in the food industry in particular. A painted surface offers only limited protection against the effects of aggressive cleaning agents and hot water, which considerably shortens the service life of plant and machinery. For example, cleaning painted gearbox housings in food industry machines repeatedly leads to the paint becoming detached from the casting, sometimes resulting in massive corrosion. In addition to the reduced load-bearing capacity, contamination in the food industry is a major exclusion criterion for machines with corroded components - resulting in machine downtime with production losses and expensive maintenance.
Limitations of previous solutions
The most widely used methods to prevent corrosion, such as electroplating or thermal spraying, reach their limits with parts that are subject to high mechanical loads and due to the lack of adhesion. Electroplated layers are relatively thin and tend to crack and flake off under mechanical stress. Thermal spraying, in which metal powder is thrown onto the surface, also shows weaknesses, as the different thermal expansion coefficients between cast iron and stainless steel can lead to stresses and thus to cracks.
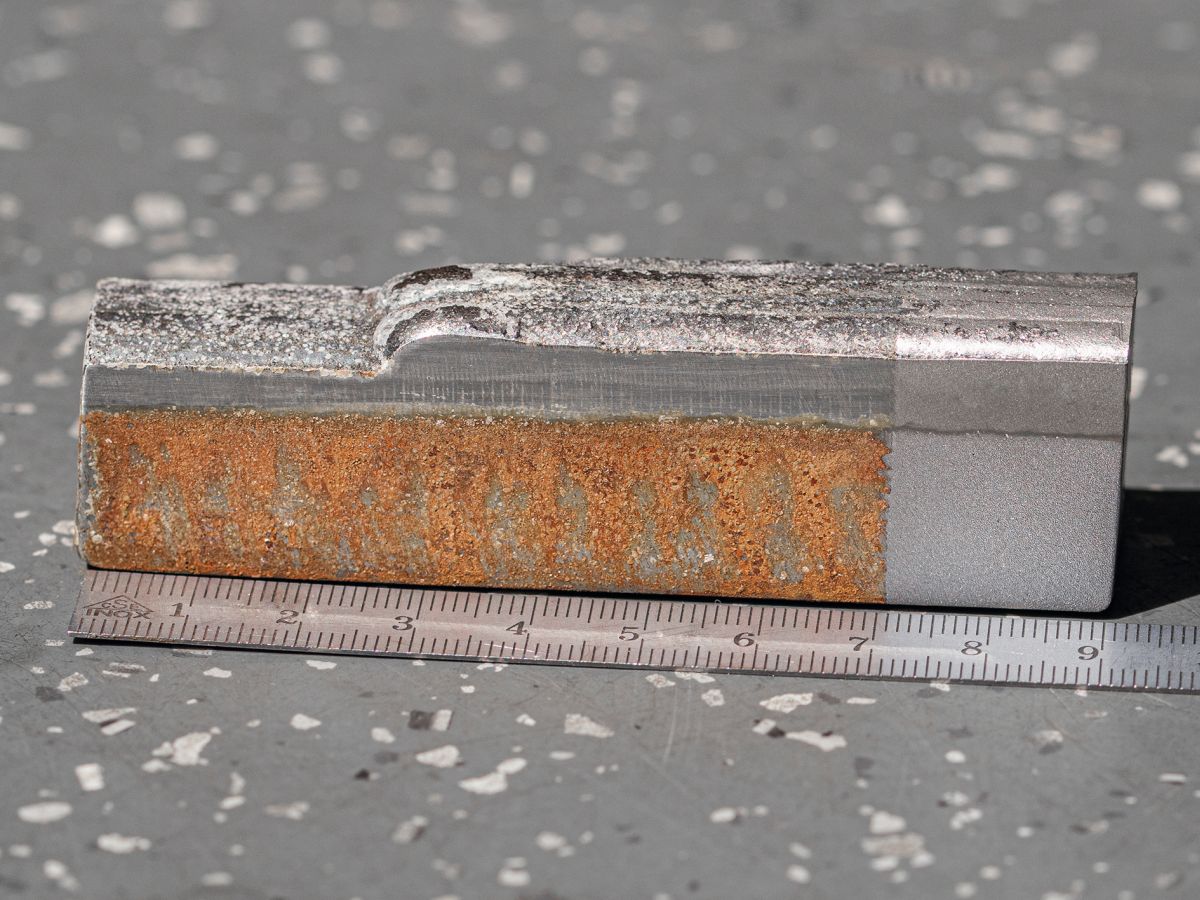 Cross-section through a cast iron test specimen to which one or two layers of stainless steel have been applied for the corrosion test
Cross-section through a cast iron test specimen to which one or two layers of stainless steel have been applied for the corrosion test
Solution approach: LMD technology
The LMD system developed by Meissner AG, the construction of which began in 2019, represents a significant improvement on previous processes. As there were no machines on the market in the desired size, Meissner AG had to develop its LMD system itself based on existing technology. It uses a laser source with a specific wavelength that enables optimum coupling of the beam into the cast iron to be coated. This is crucial, as the absorption of the laser energy depends on the alloy components of the base material and the powder to be applied.
Iron (Fe) in cast iron and, in addition to iron, chromium (Cr) and nickel (Ni) in stainless steel powder play a key role here. Iron absorbs the laser beam well, which enables efficient heat transfer and targeted melting. When coating with stainless steel, however, the absorption properties of the alloy components are also of crucial importance. Chromium and nickel not only ensure corrosion resistance, but also influence the interaction with the laser beam, as they promote absorption in the near-infrared range.
The LMD system from Meissner AG has a 4 m² machine table so that even large components can be processed safely and easily. The processing optics, from which the laser beam emerges and over which the powder of the material to be applied emerges, is guided by an industrial robot. The result is virtually restriction-free movements.
Material application and mixing
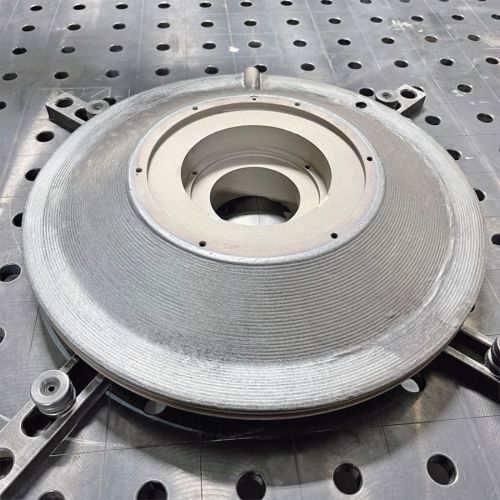 A layer of corrosion-resistant stainless steel was applied to this gearbox cover using laser cladding
A layer of corrosion-resistant stainless steel was applied to this gearbox cover using laser cladding
The material to be applied is fed into the LMD process in powder form with particle diameters of 50 to 150 µm. These particles are heated and partially melted by the laser beam as they are ejected from the nozzle and finally bond with the surface of the cast iron in the molten bath created. As laboratory tests have shown, this technology makes it possible to apply layers where the intermixing of cast iron and stainless steel is only 300 µm. This narrow transition area prevents the stainless steel from penetrating significantly into the cast iron base body, thus preserving the mechanical properties of the base material.
A key advantage of LMD technology is that only a small area of the base material is melted due to the targeted application of energy in the form of laser radiation. This avoids the large-scale thermal damage that occurs with conventional welding processes. The minimally invasive heat influence preserves the microstructural properties of the casting.
Laser radiation is characterized by its high coherence, focusability and low divergence. These properties enable a high energy density, which in the case of LMD technology is directed precisely onto the component surface. The targeted energy coupling ensures that the energy is efficiently introduced into the material, resulting in a controlled melting process. The wavelength of the laser plays a decisive role here, as the absorption of the material depends on it, among other things. A special control system in Meissner AG's LMD system ensures that the energy density is monitored and controlled at all times. This ensures that the thermal conditions are always ideally adapted to the process.
Advantages and flexibility of the Meissner AG LMD system
Meissner AG's specially developed LMD system offers a number of advantages compared to traditional welding or coating processes. The high controllability of the laser's energy density in combination with the high positionability of the processing optics by an industrial robot enables the exact dosing of the layers to be applied, which optimizes material utilization. As the powder material is only applied where it is needed, material waste is minimized. This is of particular economic importance for high-priced alloys such as stainless steel. In addition, Meissner AG's LMD system was developed in-house from the ground up. It is therefore ideally adapted to the requirements of large components, which is reflected in the cooling system, among other things. This is a decisive advantage, as even large masses of powder can be reliably welded on.
Meissner AG has also considered the reproducibility of processes and the reliable traceability of components. With the involvement of the IT department, a data logger was created which, in addition to the power values of the laser source, also stores values for temperature, humidity or measured weld pool size. Images from the pyrometer are also stored for each component, making it easier to check weld seams downstream. A system with artificial intelligence rounds off the control of the Meissner LMD system. AI can provide valuable support when running in new processes or new materials, as the operator is not fishing in the dark but can enter specific values directly.
LMD technology also offers flexibility in the design of the coating. Several layers with different properties can be applied in one process. For example, a first layer can be used to improve mechanical strength or better bonding to the base material, while the outer layer of highly corrosion-resistant stainless steel offers optimum protection against chemical influences.
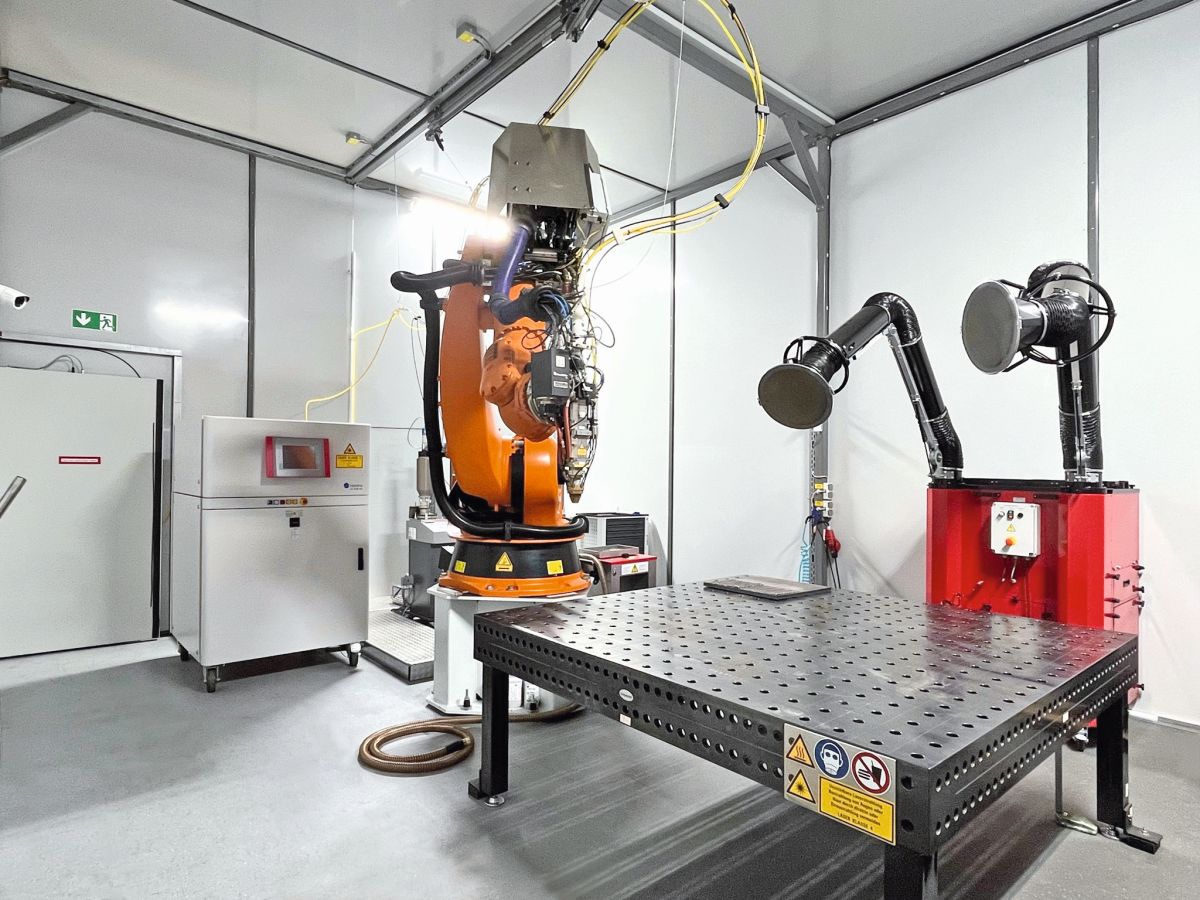 View inside the LMD system developed by Meissner AG
View inside the LMD system developed by Meissner AG
Economic and technical efficiency
In addition to the technical advantages, the material efficiency of the process leads to considerable economic savings. The targeted application of stainless steel reduces material consumption and lowers costs compared to conventional processes such as production from a stainless steel block material. Machine stands, which can traditionally be made from cast iron, retain their damping properties thanks to the LMD coating, while at the same time being reliably protected against corrosion on the surfaces subject to stress. This increases the service life of the machines and minimizes downtimes due to corrosion damage, which ultimately results in fewer production downtimes and increased turnover for the user.
Conclusion: Technological future prospects for LMD coating
Meissner AG's LMD technology represents a significant improvement in the field of cast coating. Thanks to precise laser control, optimized energy coupling and targeted material application, this method enables high-strength, corrosion-resistant coatings on cast iron without impairing its mechanical properties. The economic benefits of reduced material costs and extended service life make LMD technology a promising solution for numerous industrial applications.