Electricity from renewable energy sources in India
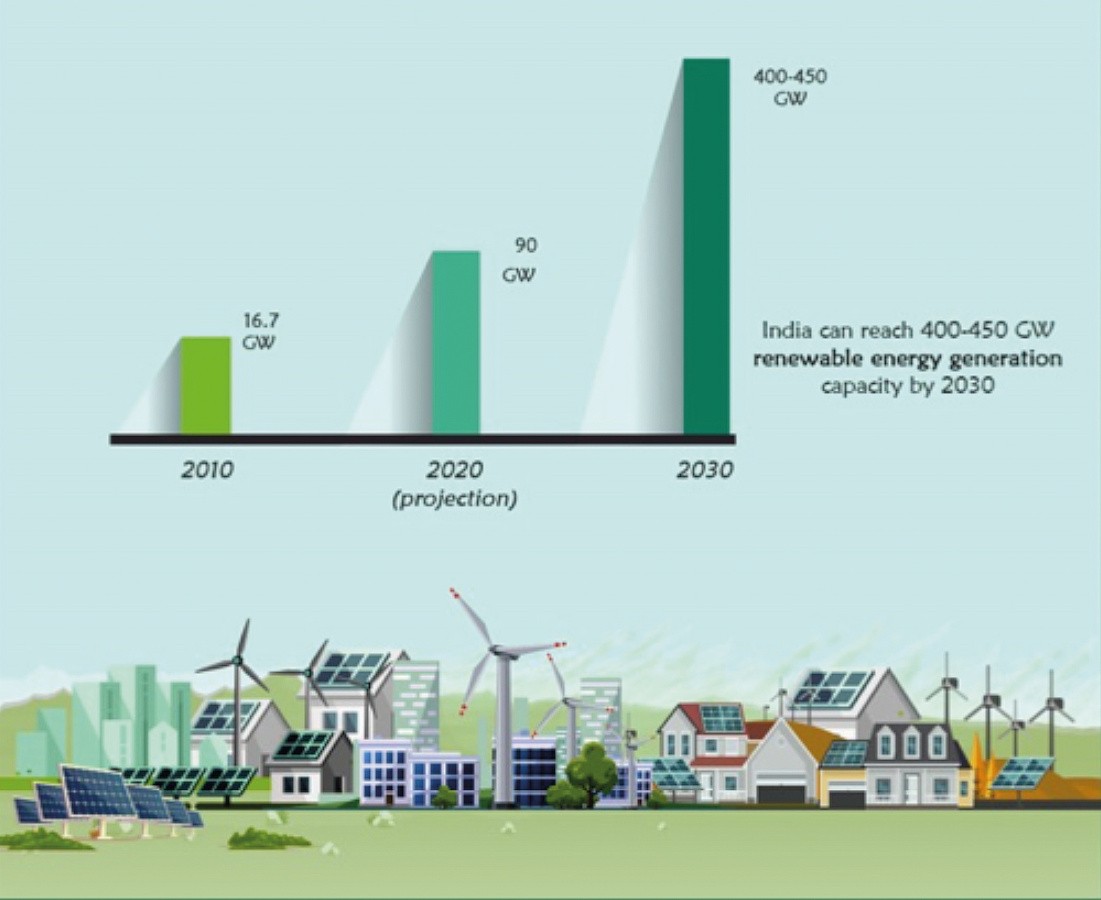
The ambitious target of generating at least 40% of total installed electricity capacity from renewable energy sources by 2030 was already achieved in India in November 2021. The government's liberal policy on foreign investment and the Green Energy Corridor (GEC) projects were the main contributing factors.
The country's total installed non-fossil energy capacity stood at 157.32 gigawatts (GW), which is 40.1% of the total installed power capacity of 392.01 GW. As of November 2021, India's installed renewable energy capacity comprised 48.55 GW of solar energy, 40.03 GW of wind energy, 4.83 GW of small hydropower, 10.62 GW of bioenergy and 46.51 GW of large hydropower. The country also has 6.78 GW of installed nuclear power generation capacity. India ranks fourth in terms of installed renewable energy capacity. India's non-fossil energy supply increased by more than 25 % in the last seven years to 40 % of the energy mix in 2021. India's solar energy grew more than 18-fold, while renewable energy capacity increased two-fold. Between 2014 and 2019, renewable energy projects received $64.4 billion in investment from the private sector. Foreign direct investment during this period amounted to around 6.4 billion euros.
Lithium batteries over the decades
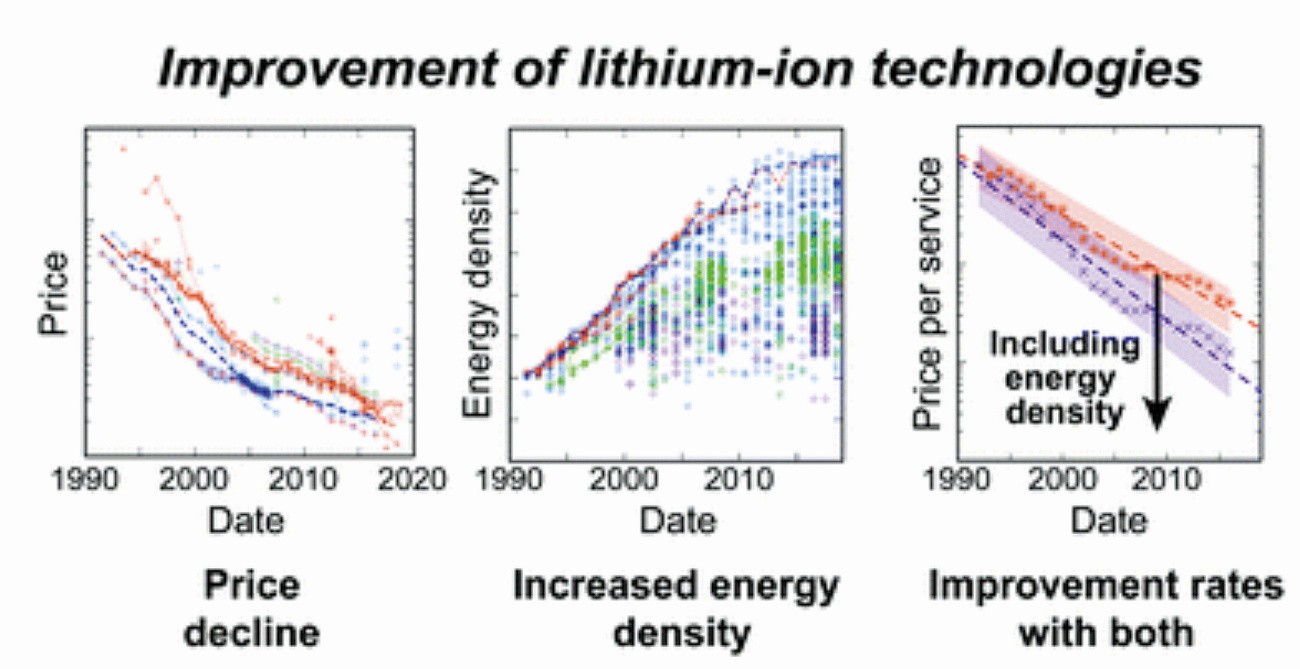
Since their introduction three decades ago, the cost of lithium-ion batteries has fallen at a similar rate to the price of solar panels - by around 97%. The main reason for this astonishing development has been the research and development work of industry and institutes, particularly in the fields of chemistry and materials science, whose profits have outstripped those from mass production. This was despite the fact that falling prices had already massively reduced costs.
Scientists from MIT and the Santa Fe Institute believe that there is still considerable room for further improvement in electrochemical battery technologies. The findings in electrical engineering, particularly in (alloy) anodes, cathodes and corrosion behavior, have contributed significantly to this. The study used an analytical approach originally developed by the authors to analyze the similar rapid decline in the cost of silicon solar cells in recent decades. They also applied the approach to understand the rising cost of nuclear energy.
Source: Energy Environ. Sci. (2021), 14, pp.1635-1651
Surface topography and antibacterial effect
It is known that surface topography influences the antibacterial properties of materials. The adhesion of bacteria to the surfaces is reduced without affecting the viability of the adhering cells.
In the case of copper-containing alloys with contact-killing properties, the adhesion of bacteria to the surface is also accompanied by interactions over short distances that regulate the toxic effect of the material surface on bacterial cells. Scientists from Shenyang, China, correlated the surface properties including different surface roughness of Cu-containing stainless steel (SS) with the bacterial damage pattern and attempted to clarify the role of surface roughness in mediating the contact-killing behavior of Cu-containing SS.
The results of the microscopic investigations by atomic force and scanning electron microscopy (AFM and SEM) showed that E. coli cells suffered the fastest physical and mechanical damage after incubation with the diamond-polished surface of Cu-containing stainless steel. The bacterial cells stiffened noticeably and the adhesion strength increased significantly. A higher exposure area for bacteria was created due to the improved hydrophobicity and higher surface potential of the diamond-polished surface, which enhanced the attractive Lewis acid-base forces and weakened the electrostatic barrier between the bacteria and the surface. In addition, contact-induced charge transfer, manifested by the release of Cu ions, and the overexpression of reactive oxygen species contribute to an efficient contact killing process, according to the authors.
Source: ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces (2021)13, pp. 2303-2315
Daimler Benz electric vehicles from India
The Indian market for electric vehicles is growing. Daimler-Benz, has been active in this market since 2020 and will soon start assembling in India. In 2022, an electric "S-Class" will be introduced, together with nine other vehicles. Local production will save 100% import duties. For some models, the waiting time in India is up to six months.