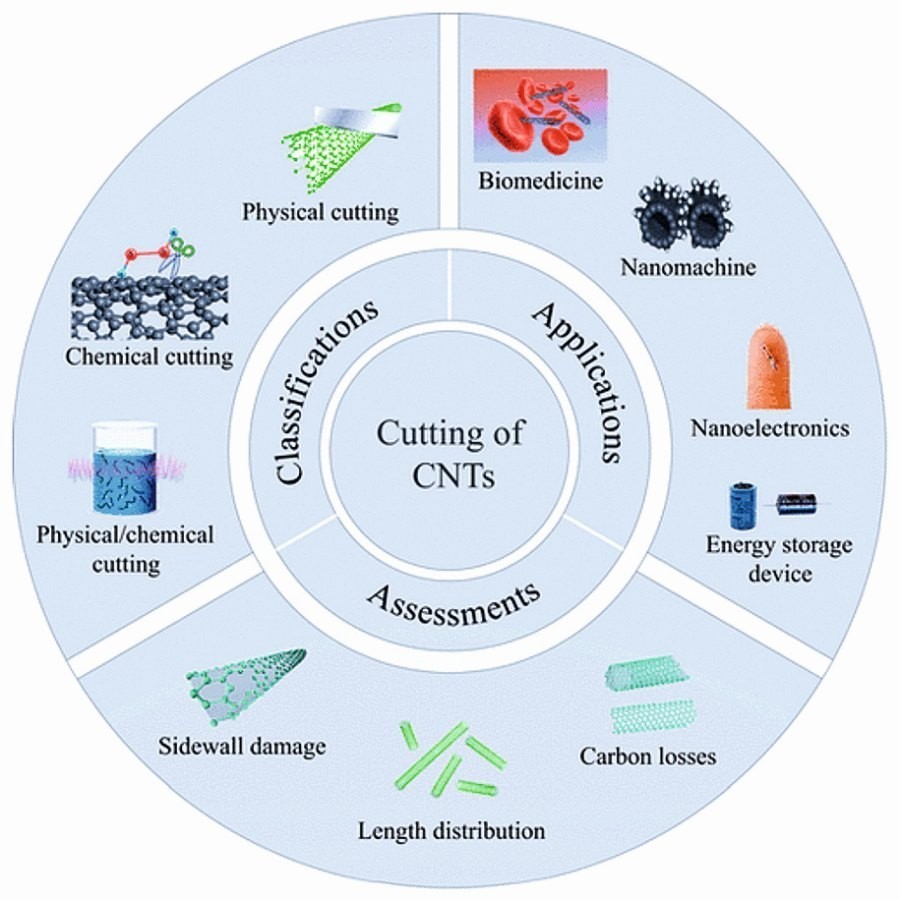
Cutting carbon nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are either single-walled (single-walled nanotubes = SWNT) or multi-walled (multi-walled nanotubes = MWNT). The SWNTs have a diameter of around one nanometer, the MWNTs up to 50 nanometers. The CNTs are mainly produced using arc discharge, laser evaporation or chemical vapor deposition. Growth initiators are used in all processes. The nanotubes obtained in this way can reach a length of micrometers, millimeters or even centimeters (as tube bundles). The differences in length and diameter, the number of walls and whether the tubes are closed or open at the ends have an influence on their chemical and physical properties and ultimately on their application.
CNTs are now used in medicine, electronics and composites. If possible, CNTs with uniform lengths should be used here. Various cutting processes have been developed to produce short CNTs. The most important methods are physical, chemical or a combination of physical and chemical methods. The most important cutting methods as well as yield, application areas and evaluation methods have been described in a review article by scientists from Shanghai University.
J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 18, pp. 9593-9617
Silver - printed and flexible electronics
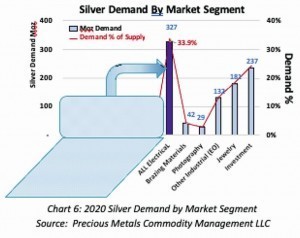
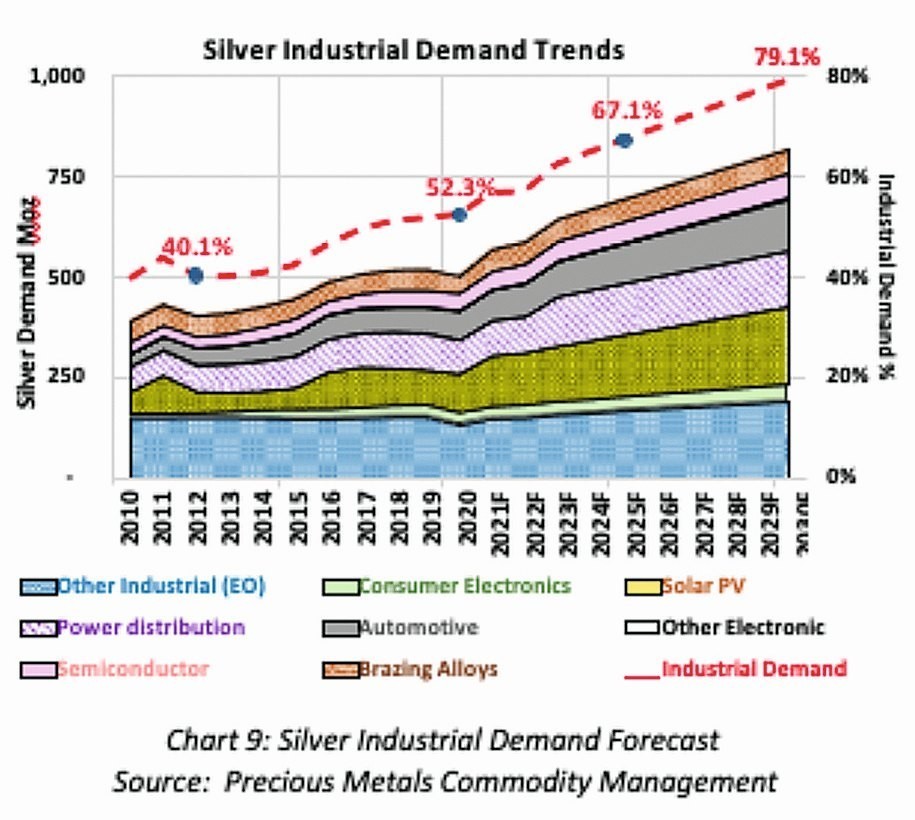
In 2020, about one third of the global supply of silver (327 million troy ounces or 10,172 tons) was consumed by the electronics industry. The electronics industry now includes consumer electronics, automotive, electrification, semiconductors, photovoltaics, power distribution, LEDs, OLEDs, MEMs and printed and flexible electronics. Silver is typically used as a coating (with or without other metals), silver and alloy paste, conductive tapes and loops, bonding wire, solder metal or solder alloy, contact material, nanoparticles, etc.
A detailed report on this topic has been published as part of the Silver Institute's 50th anniversary celebrations and can be downloaded free of charge.
https:// www.silverinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/SilverElectronics_MmktTR2021v.pdf
Industry trends 2021
Many predictions and trends made in 2019 have become less relevant due to the pandemic. This is to be expected in today's interconnected world where raw materials are produced in one country and the end products in another.
Many factors are affecting the industry in India, including shortage of components and labor, logistics and weak overall market demand. Many electronic product manufacturers have halved production after the 2nd wave of the pandemic, producing only 15 to 20 days a month. Vaccinating all employees is a priority. Alongside the pharmaceutical industry, the jewelry industry is doing best. And agriculture is looking forward to the all-important monsoon.