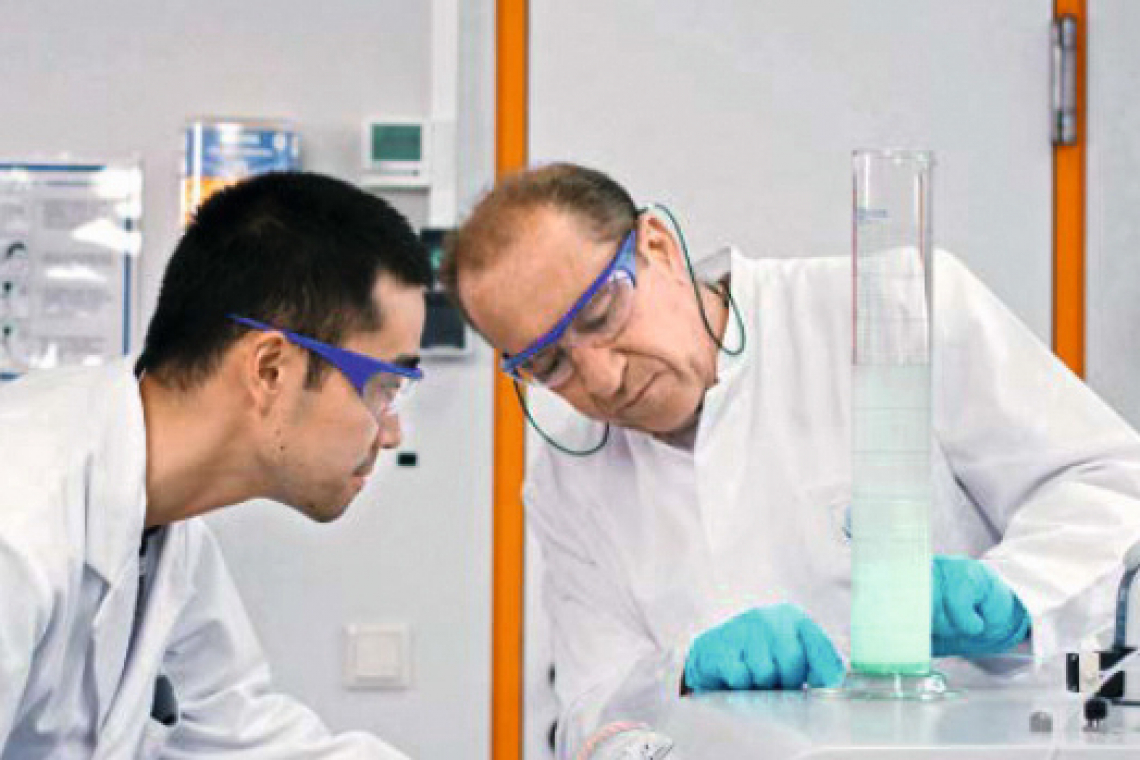
The demand for energy storage systems is growing worldwide. Lithium-ion batteries will only meet this demand to a limited extent due to the use of critical raw materials. The search for alternative battery technologies is therefore in full swing: a promising project called the "four-volt sodium-ion battery" (4NiB) aims to make progress in this area.
In this project, the Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research Baden-Württemberg (ZSW) is working with three renowned partners to develop sodium-ion batteries that are not only powerful and cost-efficient, but also represent an environmentally friendly alternative. It is planned that biowaste will also be used. The batteries are to be tailored to electric vehicles in urban traffic and stationary battery storage systems. The Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) is funding the project.
Batteries are a key element and indispensable in future scenarios for a sustainable energy supply
In the future scenarios for a sustainable energy supply, batteries are a key element and indispensable, particularly for storing electricity generated from renewable sources and for electromobility. The predicted increase in demand for energy storage from 700 GWh (2022) to 4,700 GWh (2030) requires not only the production of batteries, but also the provision of the considerable quantities of raw materials required for this. Sodium-ion batteries are currently a young but rapidly emerging technology. In these batteries, sodium takes over the role of lithium. Sodium is available in large quantities and is inexpensive, as it can be extracted from sodium chloride (sea salt), for example.