Graphene and art
Works of art deteriorate over time because they are exposed to UV and visible light, air, temperature fluctuations and humidity. With the support of the Foundation for Research and Development Hellas, scientists at the University of Patras, in cooperation with colleagues from the University of Florence, have investigated whether a kind of veil of graphene could solve this problem.
A transparent, flexible graphene film was formed using chemical vapor deposition. The layer thickness was one atom thick and the size of the layer could be varied as required. The membrane was impermeable to moisture and chemically inert. In addition, UV radiation could be absorbed to a large extent. In contrast to conventional protection methods, the protective film could be easily removed without attacking or damaging the surface of the artwork. More than 50 types of substrate were examined.
The authors of the publication speak of a protection factor of up to 70 %. If the artwork does not have a smooth surface, a graphene protective film on the protective glass can be just as effective.
Nature Nanotechnology 2021, DOI https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-00934-z
Au-As affinity
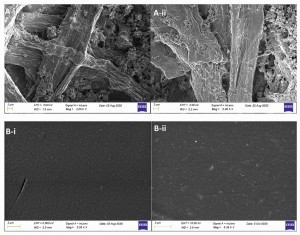 Behavior of the surface when the film is removed: cardboard before graphene coating (A-i) and after removal of the graphene film (A-ii); art paper before graphene coating (B-i) and after removal of the graphene film (B-ii) The gold mines in Karnataka (India), Salsigne (France), Sierra Nevada (USA), Snowy River (New Zealand) and Vitoria (Australia) have high concentrations of arsenic. It is known that (not only) arsenic has a high affinity to gold. The minerals pyrite and arsenopyrite absorb gold like a sponge and chemical compounds are formed.
Behavior of the surface when the film is removed: cardboard before graphene coating (A-i) and after removal of the graphene film (A-ii); art paper before graphene coating (B-i) and after removal of the graphene film (B-ii) The gold mines in Karnataka (India), Salsigne (France), Sierra Nevada (USA), Snowy River (New Zealand) and Vitoria (Australia) have high concentrations of arsenic. It is known that (not only) arsenic has a high affinity to gold. The minerals pyrite and arsenopyrite absorb gold like a sponge and chemical compounds are formed.
Thanks to the ESRF in Grenoble, an international group of geochemists now has an explanation for this. When a mineral is enriched with arsenic, gold forms a chemical compound with arsenic, roughly an Au2+ and As-1 compound, which acts as a stabilizer. If the concentration of arsenic is insufficient, gold forms only a weak compound with sulphur at the surface. According to these observations, the role of arsenic is considered to be that of a pump.
Goldschmidt Conference 2021, https://phys.org/news/2021-07-gold-arsenic.html;
doi: 10.7185/geochemlet.2112
e-waste and national security
The meaning of the term "state security" changes over time for each country. Under socialism, communism, nationalism and democracy, and during the Cold War, the term took on a different meaning each time. Currently, the US and China are seen as the two most influential countries in the world. In the past, countries were either friends or enemies. In the meantime, the distinction has become blurred. At the same time, depending on the topic, countries can be friendly and hostile ("frenemies" in German). And mistrust is on the rise.
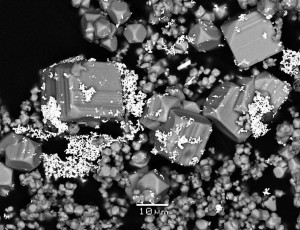 Arsenic has a high affinity with gold. Pyrite and arsenopyrite also absorb goldTherapid developments in technology, communication and transport had caused increasingly rapid globalization and polarization, with a direct impact on state security. Two developments sought to redefine the meaning of the term state security: The Covid-19 pandemic and the availability of the rare elements essential to today's highly tech-linked lifestyles. According to the United Nations, 50 million tons of e-waste were thrown away in 2019, of which only a maximum of 17% was recycled. As expected, critical raw materials, including rare earths, gold, silver, cobalt, gallium, germanium, indium and tellurium, were lost. One reason for this is the low concentrations of these elements in e-waste, which makes recovery difficult or uneconomical.
Arsenic has a high affinity with gold. Pyrite and arsenopyrite also absorb goldTherapid developments in technology, communication and transport had caused increasingly rapid globalization and polarization, with a direct impact on state security. Two developments sought to redefine the meaning of the term state security: The Covid-19 pandemic and the availability of the rare elements essential to today's highly tech-linked lifestyles. According to the United Nations, 50 million tons of e-waste were thrown away in 2019, of which only a maximum of 17% was recycled. As expected, critical raw materials, including rare earths, gold, silver, cobalt, gallium, germanium, indium and tellurium, were lost. One reason for this is the low concentrations of these elements in e-waste, which makes recovery difficult or uneconomical.
These raw materials are also very sensitive for the defense industry. As only China currently has access to rare earths, many countries see this as a threat to national security. The supply chain is classified as vulnerable.
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2021-05/tca-rcm043021.php; https://cewaste.eu/


