Scientists at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) and the National Center for Tumor Diseases Dresden (NCT/UCC), together with an international team of researchers, have succeeded in laboratory experiments in killing particularly radioresistant cancer cells from tumors in the head and neck region using a targeted immunotherapy - UniCAR T-cell therapy. The researchers developed a new molecular link that couples the UniCAR T cells to a specific surface feature of the cancer cells under investigation and thus activates them.
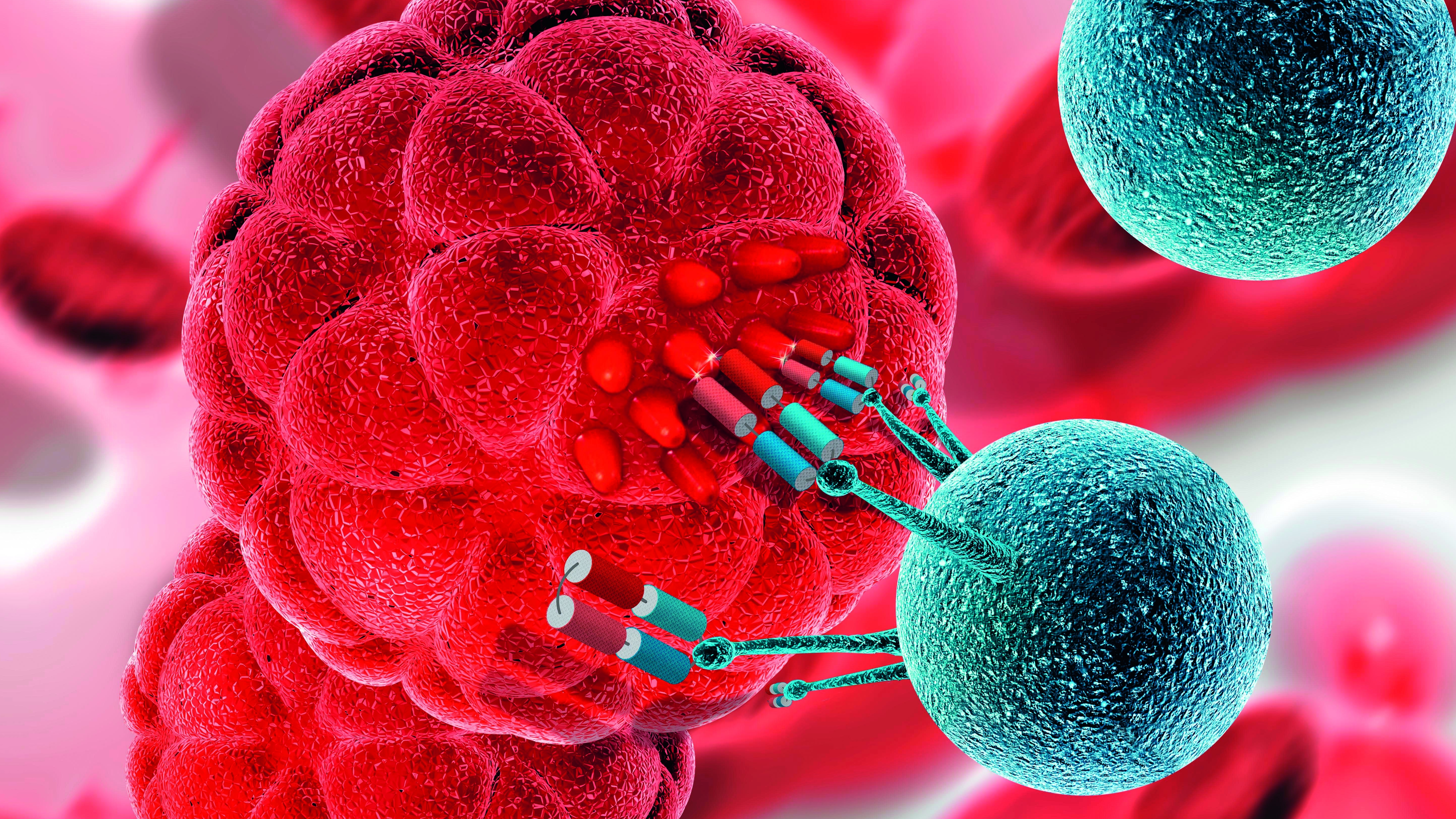
This approach is to be transferred to the imaging and treatment of viral infections, such as the new coronavirus, in a new research project. Building on this, they also want to develop universal nanosensors that could enable rapid digital diagnosis. Cancer researchers at the HZDR use bispecific antibodies to establish a link between tumor cells (red) and immune cells (blue). This approach could also be transferred to the detection and destruction of coronaviruses.
The researchers report on the results of the last three decades, in which they have developed modular, recombinant antibody derivatives that work in a similar way to a Lego brick. One end of the antibodies fits perfectly to a surface molecule of certain cells - in the established case usually cancer cells - and the other to structures in the membrane of immune cells. This method is considered promising for combating tumor diseases directly in the body.