Dispersion coatings based on chemically deposited nickel with embedded hard material particles - such as diamond, boron carbide or silicon carbide - have long been tried and tested in various industrial applications. Such coating systems exhibit excellent wear resistance. In addition to particle hardness, the properties of dispersion coatings are generally also decisively influenced by particle shape, size and distribution. Dispersion coatings for wear protection are usually 20 µm to 30 µm thick and contain 20 - 30 % hard material particles by volume.
Industrial processes for electroplating nickel-tungsten alloys with high wear protection and high ductility (e.g. "Goldeneye") are now also available on the market.
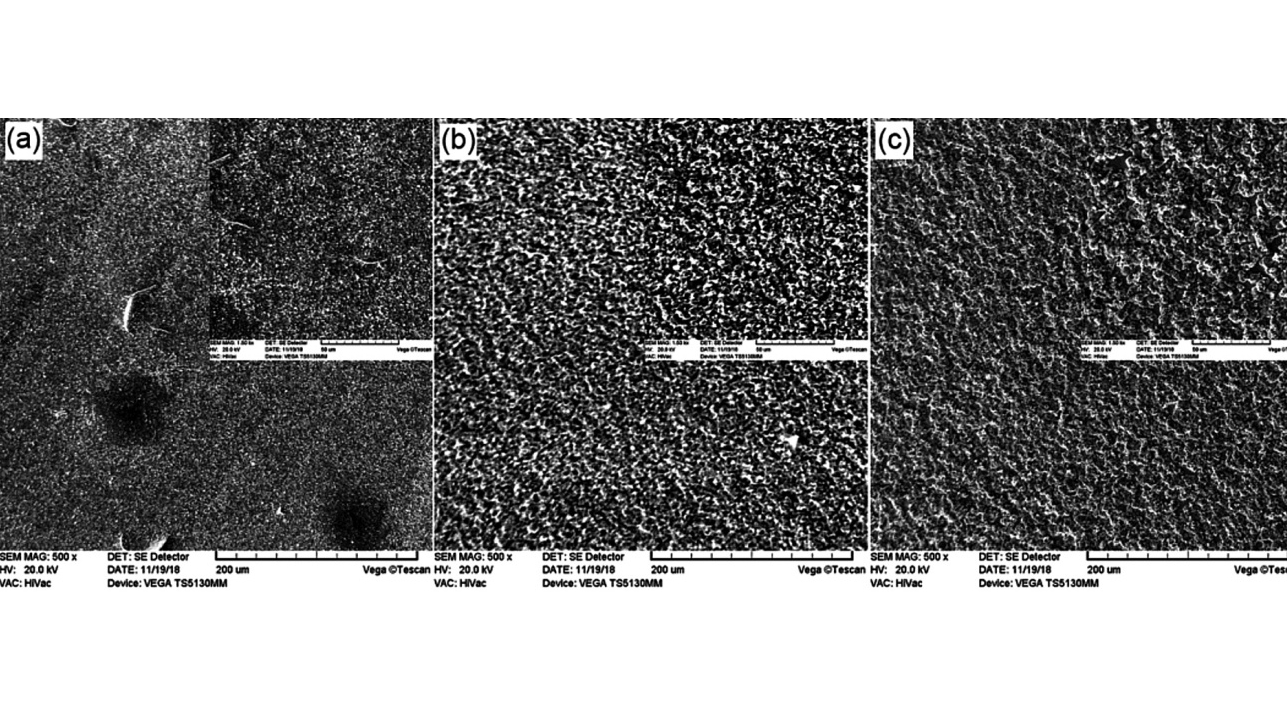
At the University of Kerman in Iran, scientists have investigated the influence of temperature on the electrolytic coating of Ni-P-W-TiO2 dispersion coatings and their microstructure, corrosion behavior and wear behavior. The electrolytic nickel-phosphorus-titanium oxide coating on the AISI 304L steel substrate was carried out at temperatures of 55 °C, 60 °C and 65 °C (Figure 1).
It was found that the coating produced at a temperature of 60 °C exhibited the highest corrosion resistance (7058 Ω.cm2) compared to the samples coated at 55 °C (2115 Ω.cm2) and 65 °C (2289 Ω.cm2). In addition, the results of the wear and microhardness test showed that the composite coating formed at 60 °C presented the highest wear resistance and microhardness (677 Vickers) compared to the samples coated at 55 °C (411 Vickers) and 65 °C (536 Vickers).
Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2022, 29, pp. 108-115
Superhydrophobic metallic soaps
Superhydrophobic (SHP) surfaces are obtained by numerous methods such as vapor deposition, etching, sol-gel technique, lithography, self-assembly, femtosecond laser pulses, electrospinning, stenciling and electrodeposition.
Chromium myristate, stearate, laurate and palmitate belong to the so-called metallic soaps. Their colloidal-chemical behavior is of great interest for the development of functional surfaces.
The acid-resistant 09CrCuSb steel (ND steel), which is often used in flue gas treatment plants, is easily susceptible to mixed acid dew point corrosion in a low-temperature flue gas environment. To improve the corrosion resistance of LP steel in a low-temperature dew-point corrosion environment, scientists in Shanghai have investigated a superhydrophobic chromium myristate hybrid (CMH) coating as a low-temperature dew-point corrosion protection coating for the LP steel substrate. This superhydrophobic coating is deposited on the LP steel substrate (pre-coated with black nickel) by DC deposition in one step. It was found that the superhydrophobic CMH coating could significantly improve the corrosion resistance of the LP substrate. This study could offer a viable strategy to prevent the mixed acid dew point corrosion of ND steel in the low temperature zone.
Materials and Corrosion 2022, 73, 6, pp. 903 - 907.
Cr(VI) extraction using emulsion liquid membranes
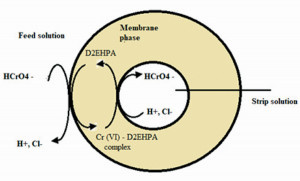 Figure 2: Extraction principle with ELM extraction processesusing emulsion liquid membranes (ELM) have attracted a lot of attention in recent years due to their potential as an effective technique for the treatment of industrial liquid waste. A major challenge here is the long-term stability of the emulsion membranes. Among other things, it is important to know the kinetics of the extraction and stripping phases. Modeling experiments play an important role here.
Figure 2: Extraction principle with ELM extraction processesusing emulsion liquid membranes (ELM) have attracted a lot of attention in recent years due to their potential as an effective technique for the treatment of industrial liquid waste. A major challenge here is the long-term stability of the emulsion membranes. Among other things, it is important to know the kinetics of the extraction and stripping phases. Modeling experiments play an important role here.
At the University of Technology and Applied Sciences in Oman, Emirates, a kinetic modeling of an emulsion fluid membrane for the extraction of hexavalent chromium from wastewater was carried out. The membrane was formed using Span 80, di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (D2EHPA) and kerosene as non-ionic surfactant, carrier and diluent, respectively (Figure 2).
The rate constants of the extraction and stripping phases were calculated by examining the effects of the HCl concentration in the feed, the concentration of the carrier in the membrane and the pH of the stripping phase. It was found that the rate of complex diffusion affects the transfer and Cr(VI) deposition in the membrane phase due to the difference between the extraction and stripping rates.
Chem. Eng. Technol. 2022, 45, 6, pp. 1141 - 1147
Miscellaneous
The Indian government is in the process of formulating a uniform specification for swappable batteries for electric vehicles. The industry has expressed concerns about a battery monopoly potentially stifling innovation.
Accton Technology Corporation, based in Taiwan's Hsinchu Science Park, is planning to set up a new production facility in Vietnam and build a back-end assembly plant in India as part of its diversification drive. Accton is known worldwide as a specialist in network switches.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation will invest around 2.2 billion Indian rupees (27 million euros) in a new factory in Pune, India. The new factory will be built in the subsidiary Mitsubishi Electric India Pvt. Ltd. and is expected to be operational in December 2023.


